|
Home | Overview | Lesson One | Lesson Two | Lesson 3 | Lesson 4 | Lesson 5
Animal Database | Assessments | Desert Causes Database | Desert People
Plant Adaptation Database | Terrain Database | Vocabulary Database
AIM: What is a desert?
MOTIVATION:
1. Ask students if they have ever
been to a desert? What was it like? Have they ever seen pictures of
a desert? What are some things you might expect to see in a desert?
Brainstorm with the students and create a semantic web to place on the board.
The following web was created on Microsoft Word and imported.
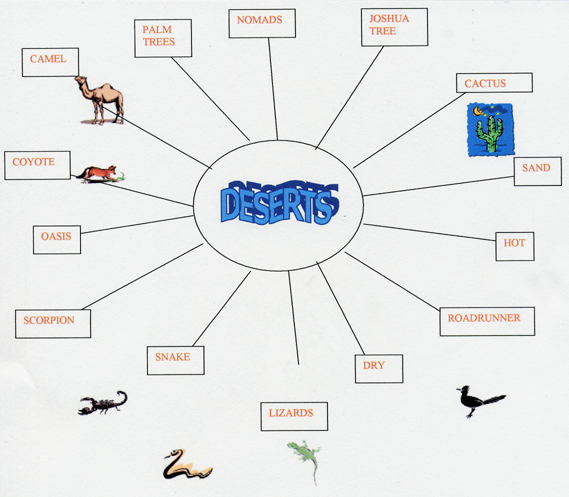
2. Create a KWL chart
after you have brainstormed with the students.
K |
W |
L |
| Deserts are
hot. |
How are
deserts formed? |
|
| Deserts are
dry. |
Why are
deserts so dry? |
|
| Animals have
to learn to live with little water. |
What kind of
animals live in the desert? |
|
| Plants have
spikes. |
What kinds
of plants grow in the desert? |
|
| Snakes live
in the desert. |
Do people
make their homes in the desert? |
|
| Cactus grows
in the desert. |
How do they
get water in the desert? |
|
| Few people
live in the desert. |
What is an
oasis? |
|
Refer to the KWL chart during the
course of the unit to assess what the students have learned and what still needs
to be covered.
3. Show the video "Desert" by
Eyewitness Video as an introduction to the desert biome
 |
Video: "Desert" by Eyewitness Video DK Publishing, Inc.
N.Y. Desert takes the viewer on a tour of the world's desert. The tape is
approximately 30 minutes long. You can
purchase it at this site: http://brainvideos.com/eyewitnesswildlife.html |
MATERIALS: Video "Desert" by
Eyewitness Videos, Internet access, word processing programs such as Microsoft
Word or Apple Works, database sheet, and printer.
PROCEDURE:
1. Define the desert biome as areas on the Earth
that receive less than 10 inches of precipitation a year. Make sure
children understand precipitation to mean rain, sleet, snow, etc.
2. Introduce vocabulary related to the desert:
desert, desertification, cactus, succulent, nomads, irrigation, oasis, sand dune, dromedary, caravan, and erosion. |
Children can use http://m-w.com (Merriam-Webster online) or http://dictionary.com to
find the definitions for these words.
3. Have children use the Internet and online
encyclopedias to research the desert biome using the vocabulary as keywords.
The following sites give basic information on an elementary level:
http://library.thinkquest.org/28855/des_what.html?tqskip1=1&tqtime=0118
http://richmond.edu/~ed344/webunits/biomes/desert.html
http://mbgnet.mobot.org/sets/desert/index.htm
4. Create a database from the vocabulary words,
using pictures from the following Internet site as illustrations. http://dgl.microsoft.com/?CAG=1 (Teachers
need to click "accept" to gain access).
Children will fill in the database from their online research. The
following is for teacher use. A student database can be found by clicking here.
KEYWORD |
FACTS |
DESERT |
Any
large area where the rainfall is less than 10 inches a year. |
CACTUS |
Every single kind of cacti is a succulent. Cacti have separate areoles
for each spine but some succulents are linked altogether. |
NOMADS |
Nomads are people who move from one place to another. Nomadism is a cycle,
as people move to this place to another, they may go back to the previous
place again after a length of time, for living things there will grow again
after some time. |
OASIS |
A
fertile or green spot in a desert or wasteland, made so by the presence of
water. |
SAND DUNE |
Sand
moved by wind. These formations can vary from small heap-like
structures on only a yard in height to enormous sand mountains over
thousands of feet high. |
DROMEDARY |
Camels are large mammals that live in dry areas. There are two types of
camels: the one-humped camel (the Arabian Camel or Dromedary)
|
5. Students will go to the following sites and
fill in the database on what a desert is:
http://mbgnet.mobot.org/sets/desert/index.htm
Again, a student copy can be found by clicking here.
What is a desert like? |
The desert is often very hot in
the daytime.
 At night, it may
get somewhat chilly, or even cold. At night, it may
get somewhat chilly, or even cold.
 Here at the
virtual desert it is 100 degrees during the day and drops to 50 degrees
at night. Here at the
virtual desert it is 100 degrees during the day and drops to 50 degrees
at night.
|
|
What causes a desert? |
Most deserts are found in bands along
30 degrees latitude north and 30 degrees latitude south (between the dotted
lines on the map).
Other deserts are caused by what is called the "rainshadow"
effect. As air moves up over a mountain range, it gets cold and loses the
ability to hold moisture -- so it rains or snows. When the air moves down
the other side of the mountain, it gets warmer. Warm air can hold lots of
moisture, so it doesn't rain as much, and a desert is formed. Click
here for a good diagram on desert formation. |
What are the two types of
desert? |
Deserts come in two varieties:
hot and cold.
|
ACTIVITY:
Students will create a
bar graph comparing the annual
rainfall in inches between the desert biome and the six other major biomes on
Earth. They will get the information from http://mbgnet.mobot.org/sets/desert/index.htm and use the following
site to make their graph. They will name their graph "Comparison of Biome
Rainfall".
http://nces.ed.gov/nceskids/Graphing
An example of a graph created at this site:
FOLLOW-UP:
1.
Have children answer the following questions on what a desert is:
a. What is the definition of a desert?
b. How do deserts compare in rainfall to the other biomes?
c. What are two causes of deserts?
d. What are the two types of deserts?
This lesson will lead to Lesson 2 -"Desert
Geography"
|