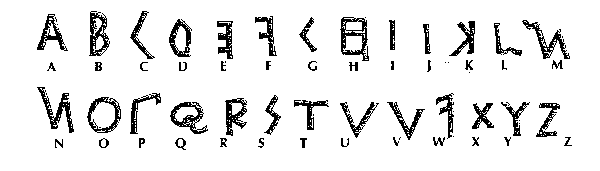
The letters K, Y and Z weren't used very often. The letter J was the same as I, and U the same as V.
Home Geography History Family Architecture Religion Science & Technology Resources
Rubric for Lessons on Roman Family Life
Answers to Table and Rubric
|
|
Name Called |
Clothes |
Schooling |
Food |
Fun |
Homes |
|
Rich People |
Patricians
Soldiers |
Colorful Tunics and Togas,
calcei or sandals. Women wore fine stolas or robes, makeup and jewelry |
Only men and boys learned to read and write in private schools or tutors at home. They used a Wrote on wax tablets and wrote with a
stick called stylus. |
fresh meat, fish, fruits, vegetables, bread, honey and wine |
Men only bath houses, watched
gladiator fights, wrestling, chariot races Rich and Poor BOYS: Balls, board games, kites, tiny models of people and animals, hoops, with pieces of metal on them, like bells, to jingle and warn people in their way. stilts tic-tac-toe, Knucklebones" like jacks, only played with bones.The boys played war-type games. |
Large homes with many rooms called a
Domus or Villa |
|
Poor People |
Plebeians |
Tunic or robes, sandals |
No schooling |
bread, olives, cheese, raisins,
water |
GIRLS: rags dolls and dolls of wax or clay. Ball, board games and lifted weights. |
small rooms or apartments or
cenaculum |
|
Slaves |
Slaves |
Tunics and sandals |
slaves taught kids at home |
|
|
small rooms in owners houses or
prisons. |
|
|
Rich Men |
Poor Men |
Rich Women |
Poor Women |
Rich Boys |
Poor Boys |
Rich Girls |
Poor Girls |
|
|
Head of family, |
shopkeepers, farmers, and
craft workers. |
Ran their home and children |
Ran their home and worked with husband |
Went to private school or had tutors at home.
Learned to read and write. |
learned family business Were considered men at
16 |
learned to sew, weave and run a
home, got married at 14 |
learned family business got married at 14 or 15 |
Home Geography History Family Architecture Religion Science & Technology Resource
Roman Numerals Activity
1=I
2=II 3=III 4=IV 5=V
6=VI 7=VII 8=VIII 9=IX
10=X
11=XI 12=XII
13=XIII 14=XIV 15=XV
16=XVI 17=XVII 18=XVIII
19=XIX
20=XX
352=MMMLII 3501=MMMDI
45 =VL 150
=CV 1500= MD
2004=
MMIV
Use regular grading scale
Home Geography History Family Architecture Religion Science & Technology Resources
Comparison of Latin & English Alphabets
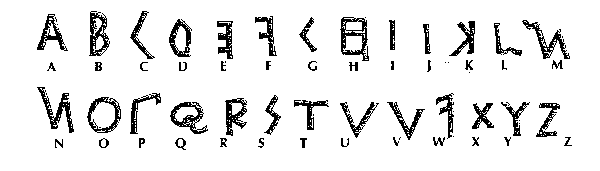
The letters K, Y and Z weren't used very often.
The letter J was the same as I, and U the same as V.
Comparison Paragraph
|
CATEGORY
|
4
|
3
|
2
|
1
|
|
Introduction (Organization)
|
The introduction is inviting, states the main topic and previews the
structure of the paper.
|
The introduction clearly states the main topic and previews the structure
of the paper, but is not particularly inviting to the reader.
|
The introduction states the main topic, but does not adequately preview
the structure of the paper nor is it particularly inviting to the reader.
|
There is no clear introduction of the main topic or structure of the
paper.
|
|
Focus on Topic (Content)
|
There is one clear, well-focused topic. Main idea stands out and is
supported by detailed information.
|
Main idea is clear but the supporting information is general.
|
Main idea is somewhat clear but there is a need for more supporting
information.
|
The main idea is not clear. There is a seemingly random collection of
information.
|
|
Sequencing (Organization)
|
Details are placed in a logical order and the way they are presented
effectively keeps the interest of the reader. Describes all differences
and similarities
|
Details are placed in a logical order, but the way in which they are
presented/introduced sometimes makes the writing less interesting
Describes a few similarities and difference..
|
Some details are not in a logical or expected order, and this distracts
the reader. Describes 1 similarity and 1 difference
|
Many details are not in a logical or expected order. There is little sense
that the writing is organized. Is not clear on similarities and
differences.
|
|
Transitions (Organization)
|
A variety of thoughtful transitions are used. They clearly show how ideas
are connected.
|
Transitions clearly show how ideas are connected, but there is little
variety.
|
Some transitions work well; but connections between other ideas are fuzzy.
|
The transitions between ideas are unclear or nonexistent.
|
|
Grammar & Spelling (Conventions)
|
Writer makes no errors in grammar or spelling that distract the reader
from the content.
|
Writer makes 1-2 errors in grammar or spelling that distract the reader
from the content.
|
Writer makes 3-4 errors in grammar or spelling that distract the reader
from the content.
|
Writer makes more than 4 errors in grammar or spelling that distract the
reader from the content.
|
|
Sentence Structure (Sentence Fluency)
|
All sentences are well-constructed with varied structure.
|
Most sentences are well-constructed with varied structure.
|
Most sentences are well-constructed but have a similar structure.
|
Sentences lack structure and appear incomplete or rambling.
|
http://rubistar.4teachers.org/index.php
Home Geography History Family Architecture Religion Science & Technology Resources